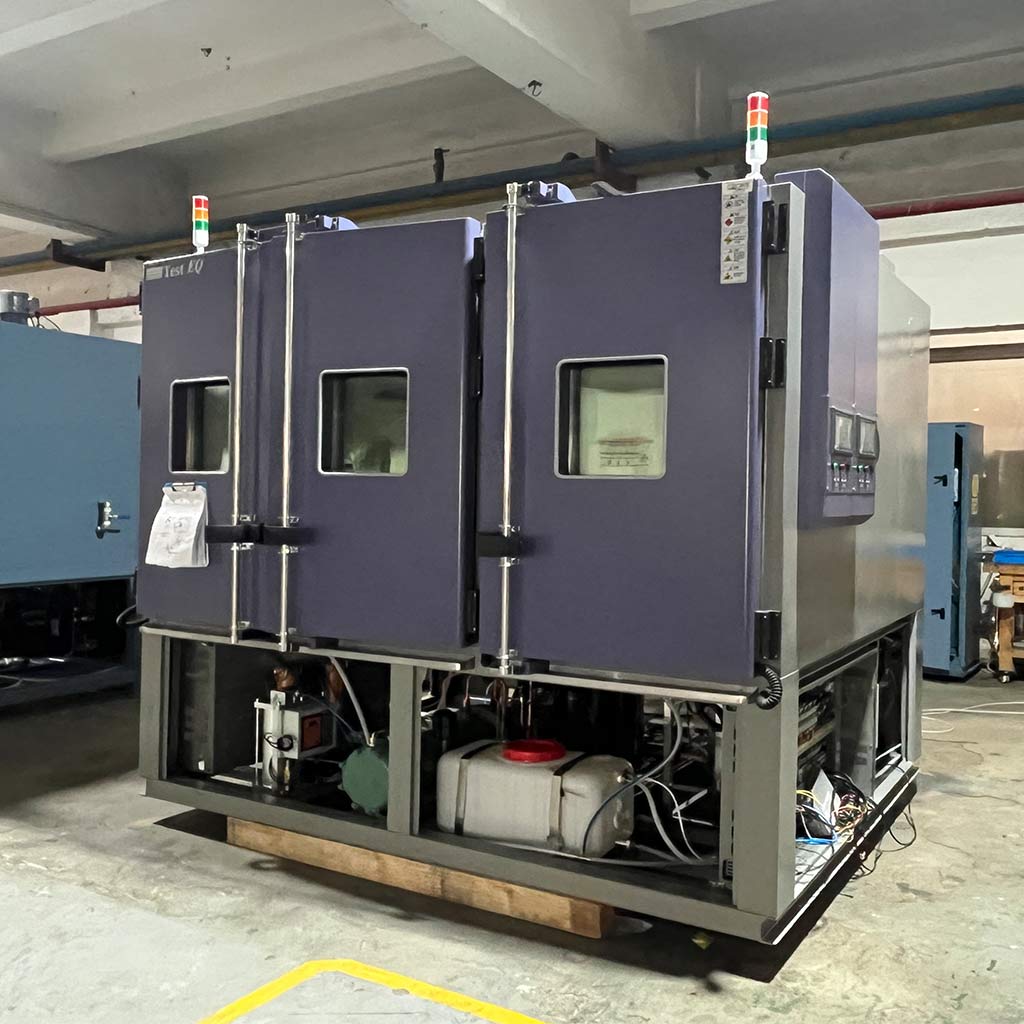

2026-01
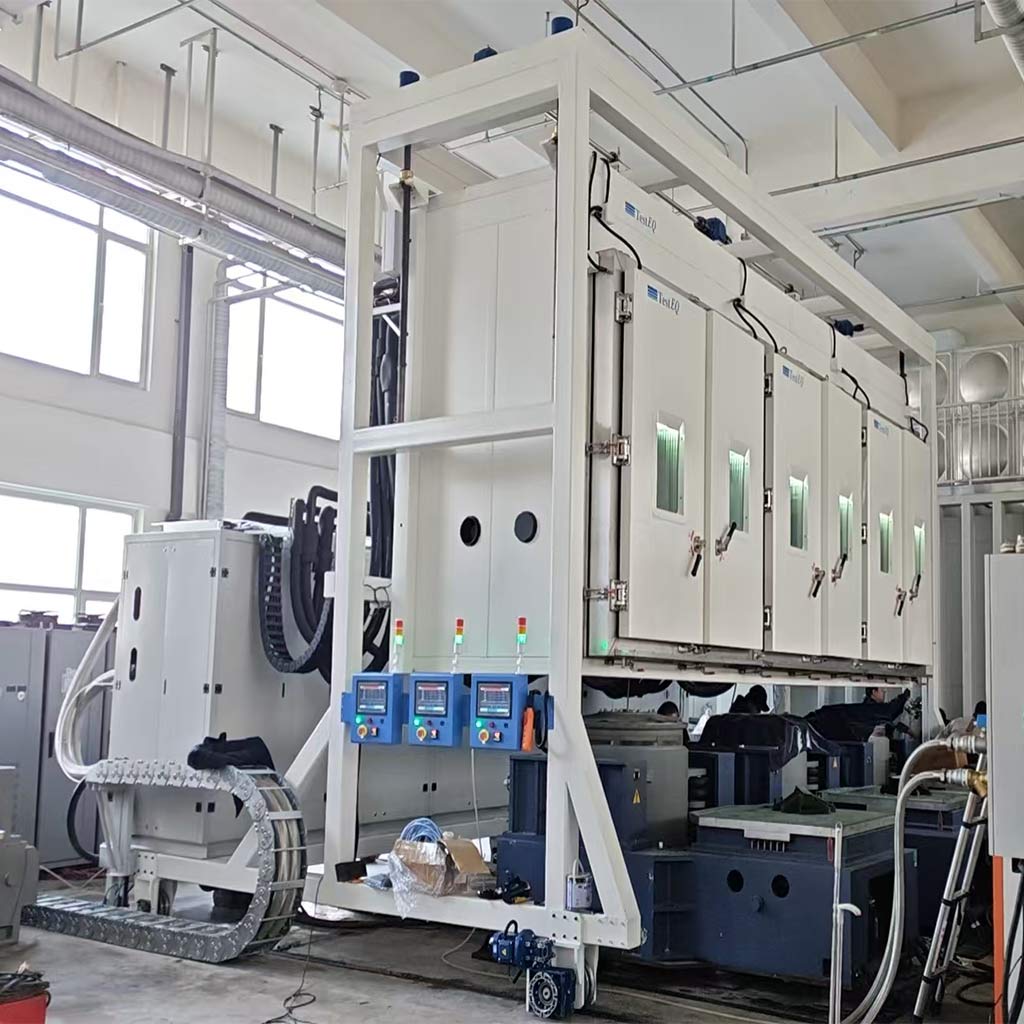

2026-01
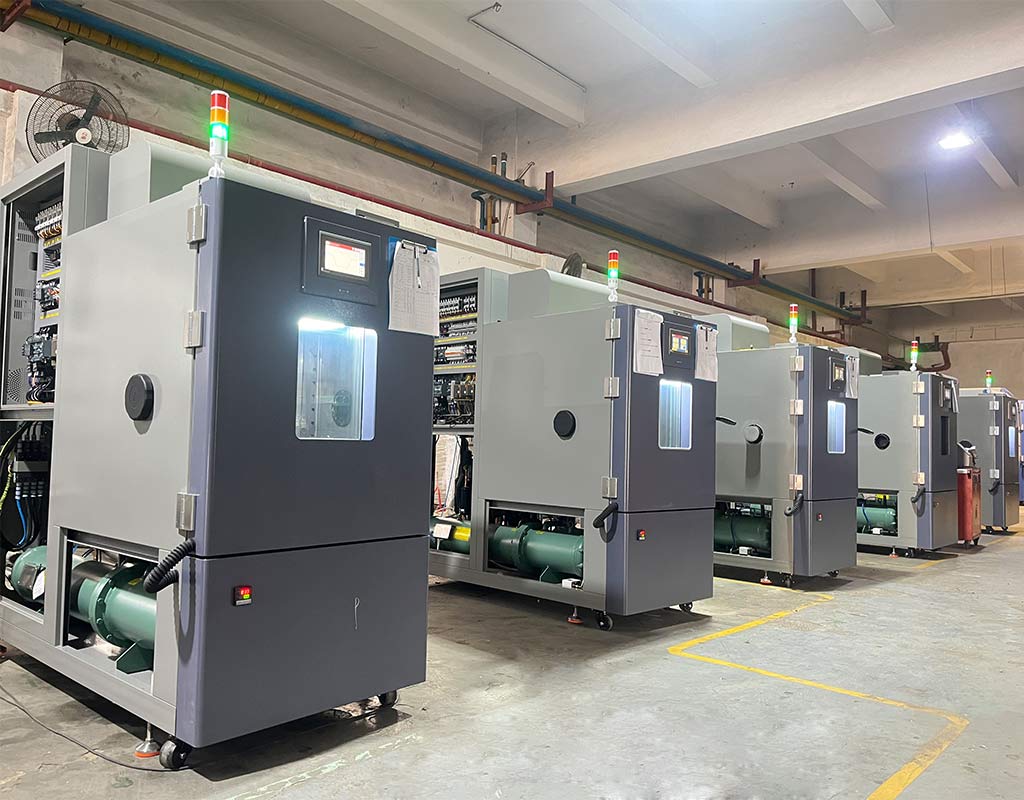

2025-12
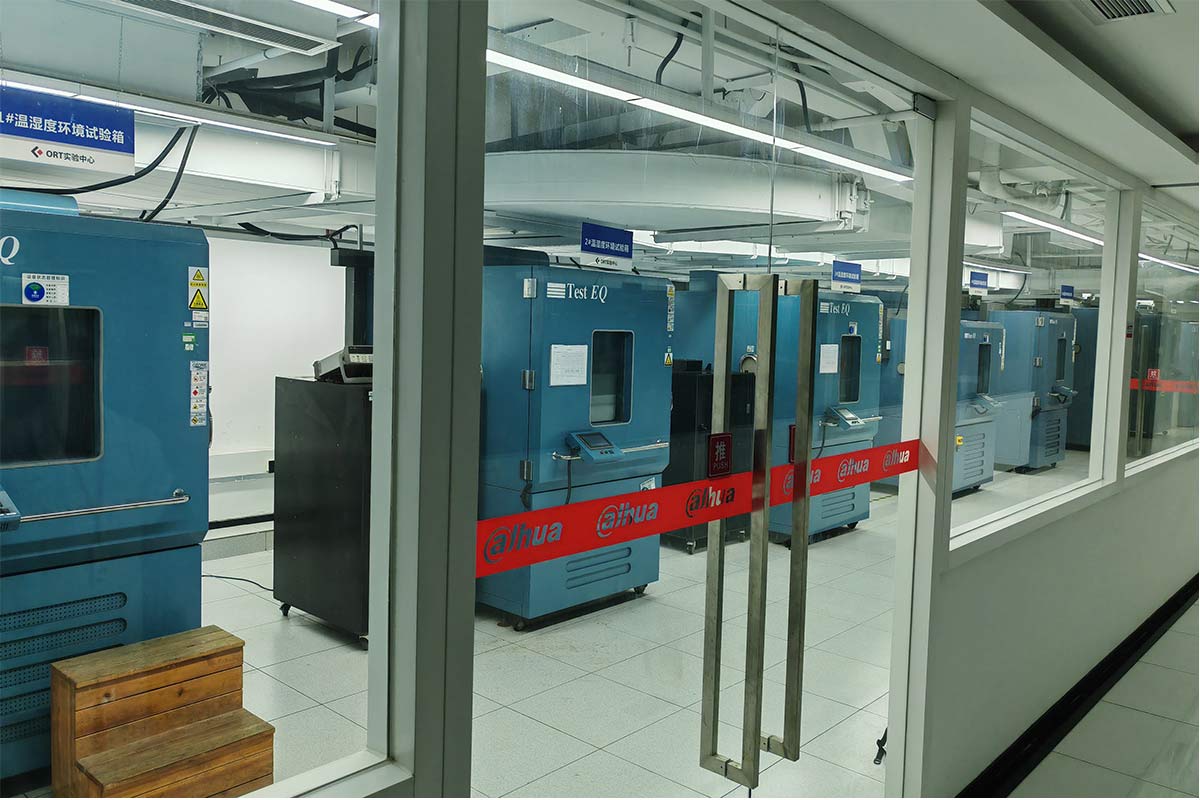

2025-12
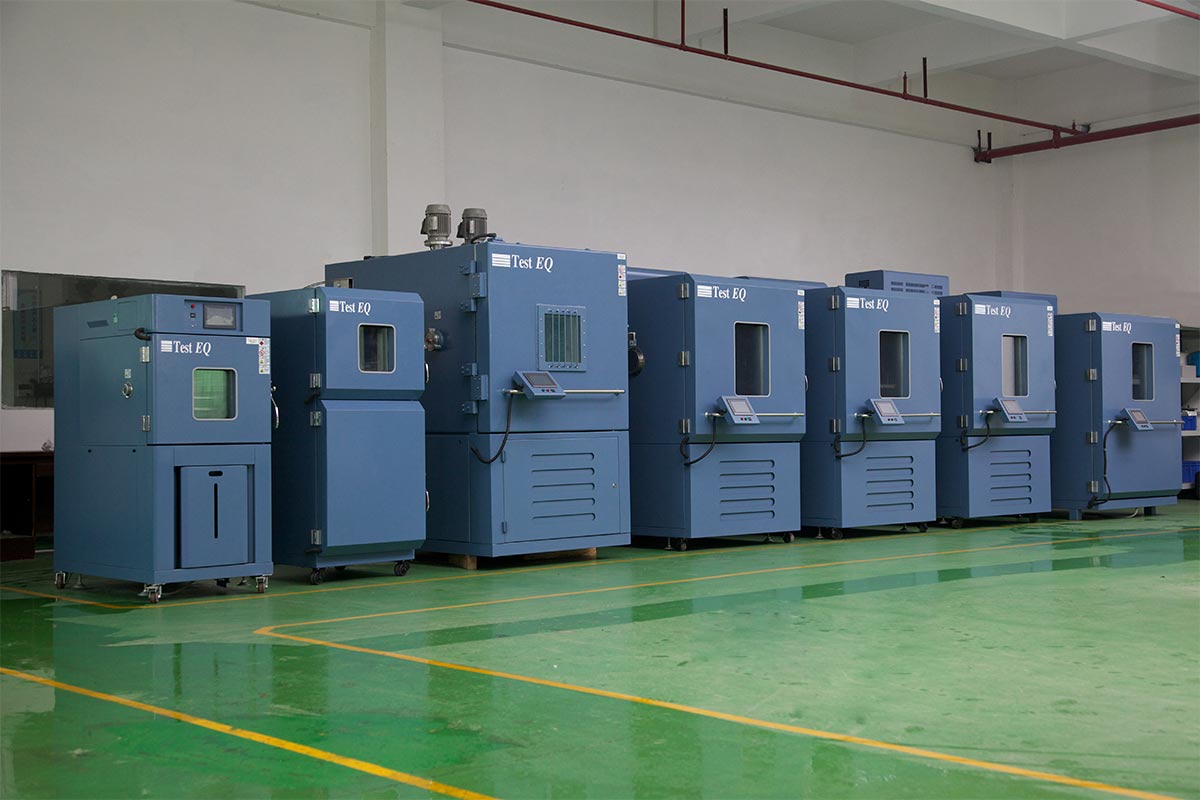

2025-12
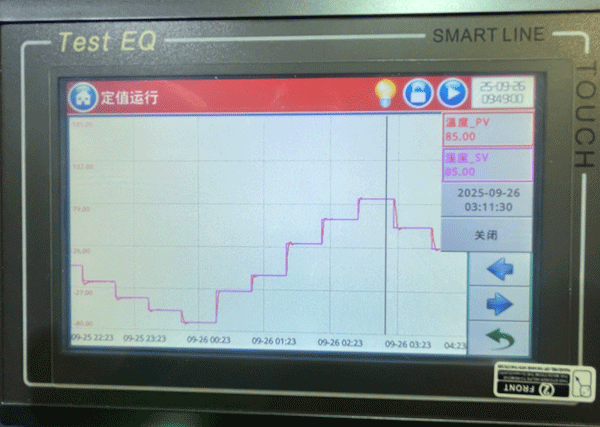
2025-09
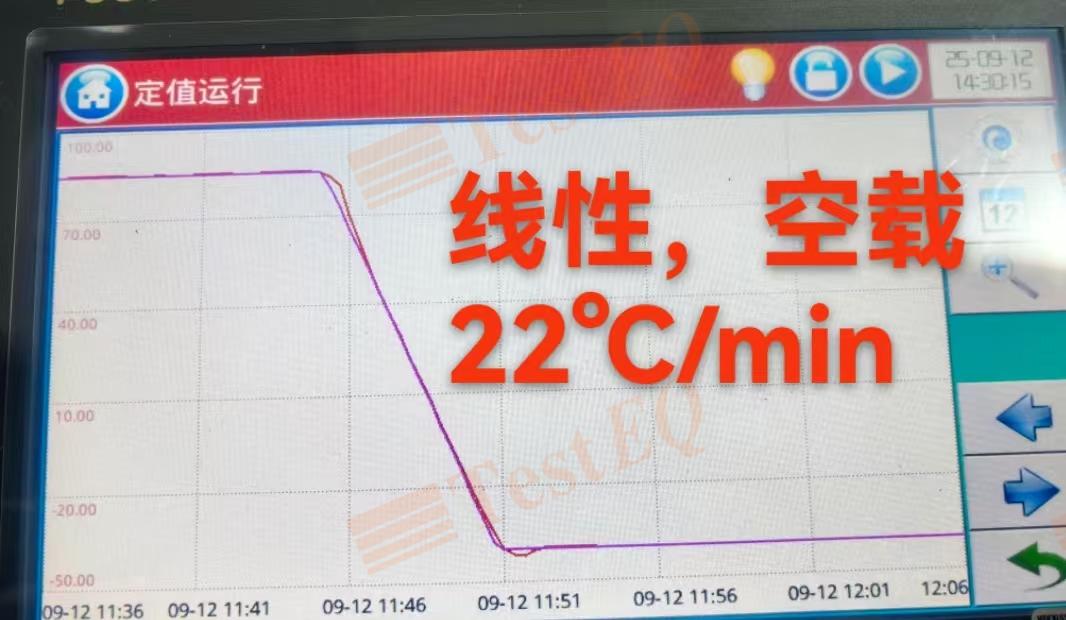
2025-09
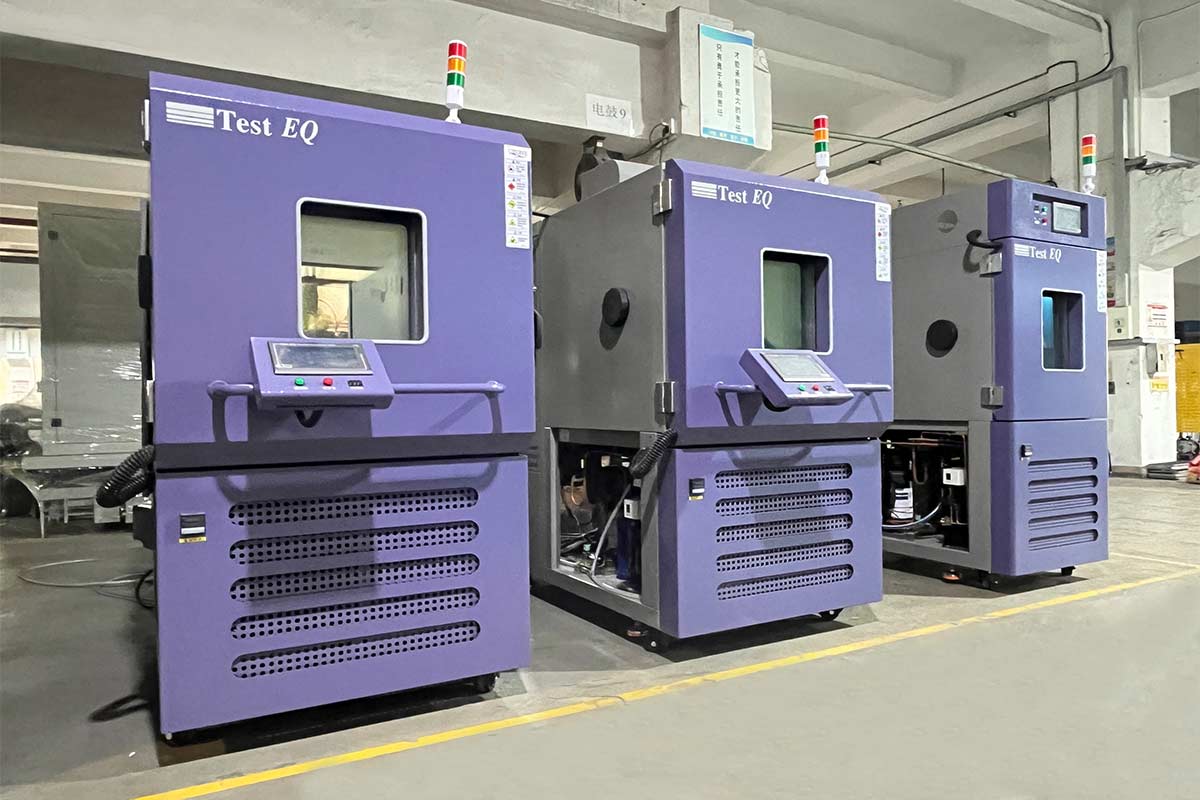

2025-09

2025-09

2025-08
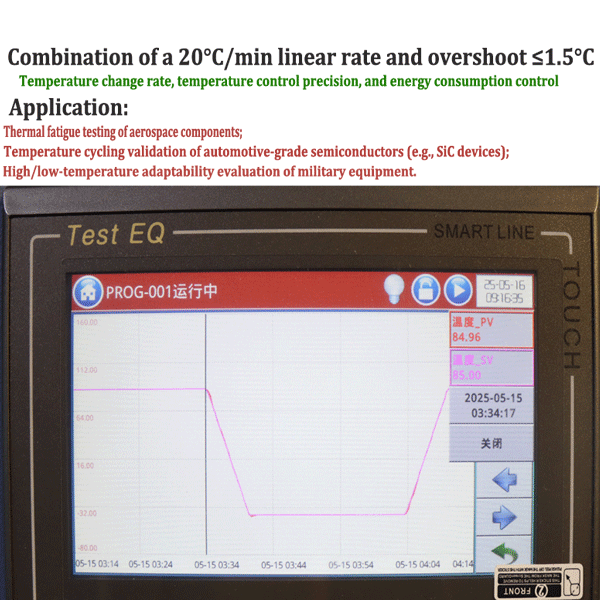
2025-08
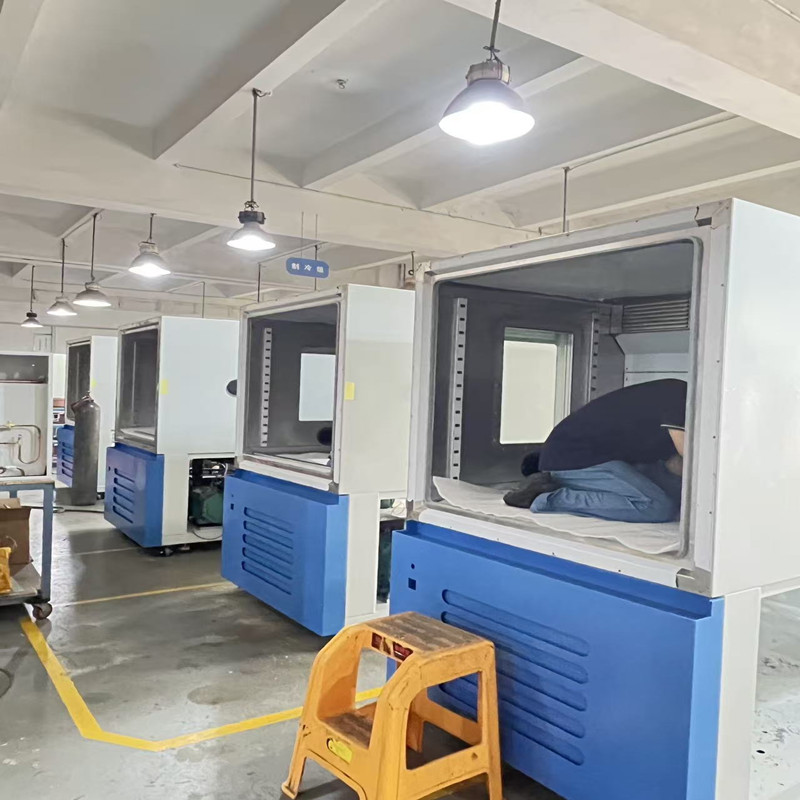

2025-08
We will contact you within 1 working day, please pay attention to the email with
the suffix "@test-eq.com".
We will contact you within 1 working day, please pay attention to the email with the suffix "@test-eq.com".
P.IVA: 91441900MAECQJHY37 Guangdong Test EQ Equipment Co., Ltd. | All Rights Reserved